In recent years, the world has witnessed a significant surge in the number of people learning Portuguese as a foreign language. This trend is not just a passing fad but a reflection of the growing importance of Portuguese on the global stage. Whether it’s for business, travel, or cultural enrichment, there are numerous compelling reasons to take up Portuguese. In this blog post, we will explore ten key reasons why Portuguese is becoming increasingly popular and why you should consider learning it too.
1. Portuguese is a Global Language
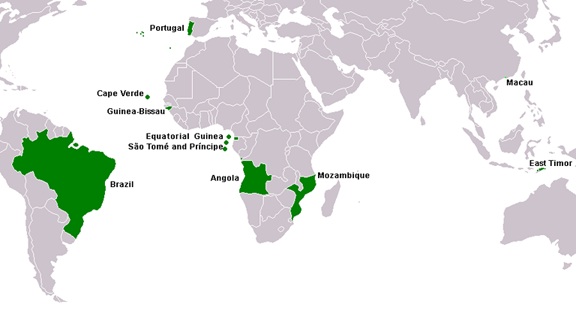
Portuguese is the sixth most spoken language in the world, with over 220 million native speakers. It is the official language of nine countries (plus Macau), including Brazil, Portugal, Mozambique, Angola, and several others. This widespread use makes Portuguese a valuable language for international communication and opens up opportunities in various regions across the globe.

2. Economic Opportunities in Brazil
Brazil, the largest Portuguese-speaking country, boasts one of the world’s largest economies. With its diverse industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and technology, Brazil offers numerous business opportunities. Learning Portuguese can give you a competitive edge in the job market and help you tap into the economic potential of this vibrant country.
3. Rich Cultural Heritage
Portuguese-speaking countries have a rich cultural heritage that spans literature, music, dance, cinema, and cuisine. From the soulful sounds of Fado music in Portugal to the vibrant Carnival celebrations in Brazil, learning Portuguese allows you to immerse yourself in these unique cultural experiences and gain a deeper appreciation for the traditions and customs of these countries.
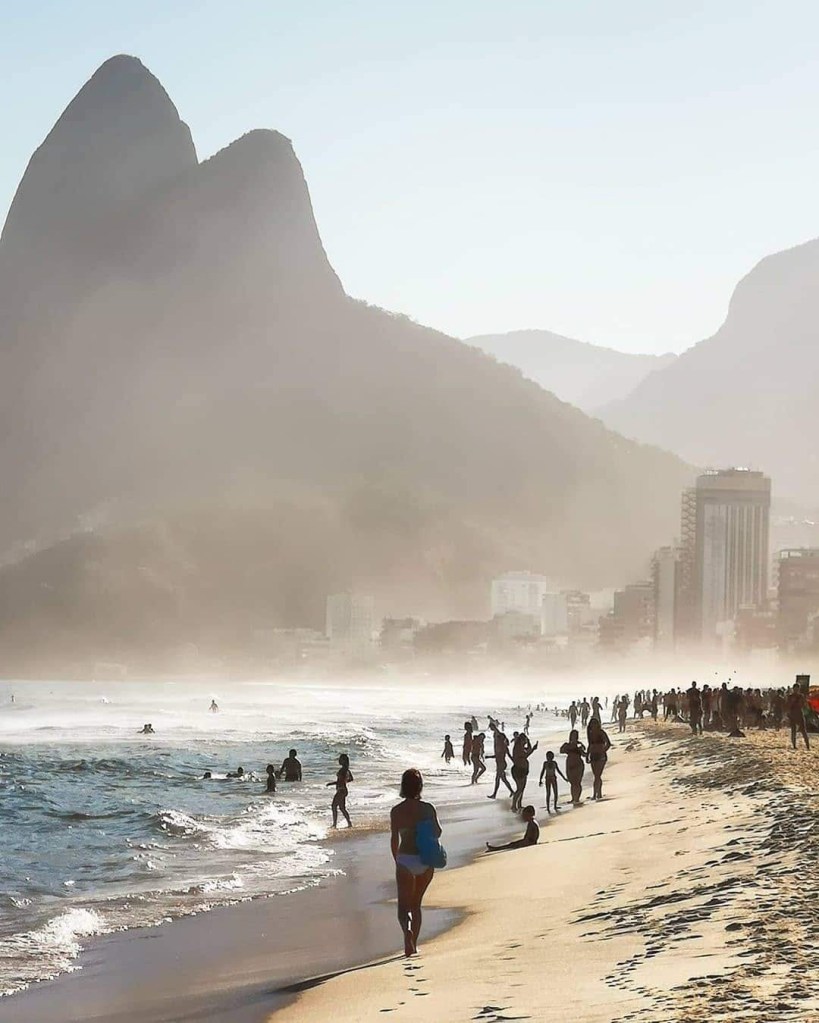
4. Travel and Tourism
Portuguese-speaking countries are popular travel destinations, known for their stunning landscapes, historical landmarks, and warm hospitality. Whether you’re exploring the picturesque streets of Lisbon, relaxing on the beautiful beaches of Rio de Janeiro, or embarking on a safari in Mozambique, knowing Portuguese can enhance your travel experiences and help you connect with locals on a more personal level.

5. Academic and Research Opportunities
Portuguese is an important language in academia and research, particularly in fields such as Latin American studies, linguistics, and history. Many universities and research institutions offer programs and scholarships for students who are proficient in Portuguese. By learning the language, you can access a wealth of academic resources and collaborate with scholars from Portuguese-speaking countries.
6. Growing Influence in Africa
Portuguese is an official language in several African countries, including Angola, Mozambique, and Guinea-Bissau. These countries are experiencing rapid economic growth and development, making them attractive destinations for investment and business ventures. Learning Portuguese can help you navigate these emerging markets and build strong connections with local partners.

7. Enhanced Cognitive Skills
Learning a new language has been shown to improve cognitive skills, such as memory, problem-solving, and multitasking. Portuguese, with its unique grammar and vocabulary, can provide a stimulating mental workout and keep your brain sharp. Additionally, being bilingual or multilingual can enhance your overall communication skills and cultural awareness.

8. Access to Portuguese Literature and Media
Portuguese literature is rich and diverse, with renowned authors such as Fernando Pessoa, José Saramago, Machado de Assis and Clarice Lispector. By learning Portuguese, you can read these literary works in their original language and gain a deeper understanding of their nuances and cultural context. Additionally, you can enjoy Portuguese-language films, music, and television shows, further enriching your cultural experience.

9. Strengthening Personal and Professional Relationships
Knowing Portuguese can help you build stronger personal and professional relationships with Portuguese-speaking individuals. Whether you’re working with colleagues from Brazil, making friends in Portugal, or collaborating with partners in Angola, speaking their language can foster trust, respect, and effective communication.
10. A Fun and Rewarding Challenge
Learning Portuguese can be a fun and rewarding challenge. The language has a melodic quality and a rich vocabulary that can be enjoyable to learn and use. As you progress in your language journey, you’ll experience a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction that comes with mastering a new skill.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are countless reasons to take up Portuguese as a foreign language. From economic opportunities and cultural enrichment to travel and cognitive benefits, learning Portuguese can open up a world of possibilities. So why not embark on this exciting linguistic adventure? Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply a language enthusiast, Portuguese is a valuable and rewarding language to learn. Start your journey today and discover the many benefits of speaking Portuguese!
Note: Jorge Sette, M.A. in Applied Linguistics offers lessons of Brazilian Portuguese online. The number of spots is limited. Hurry up! Don’t hesitate to reach out to him at: jorge.sette@terra.com.br